[Construction] Nuclear power plant design [Operation] Safety evaluation / lifespan management

[Operation] Operation & Maintenance
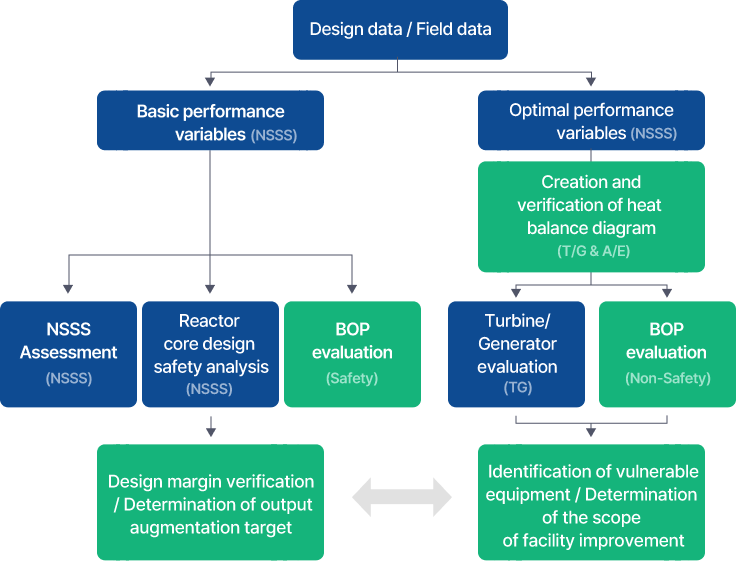
Continuous facility improvements taking into account the latest regulatory and safety requirements, even after commercial operation is essential, to improve nuclear power plants' safety and secure operation efficiency. In particular, it is essential for a design company with comprehensive design capability to perform consistent design changes to important systems such as Reactor Coolant System(RCS) and Engineered Safeguard System. Therefore, KEPCO E&C, the original designer of Korea’s nuclear reactor facilities since Hanbit Units 3 and 4, leverages its proprietary design technology to analyze problems occurring in all domestic nuclear reactor facilities in operation and delivers technical solutions. We are improving the safety of nuclear reactor facilities through facility improvement, major equipment and facility replacement, technical support for licensing, and improvement of power plant operations, in addition to performing various technical support tasks for nuclear power plant owners, such as maintaining consistent design data and configuration management.
Main business areas
Major Components Replacement and Refurbishment
- Technical support and design change work for replacing major components due to aging after the prolonged operation of the relevant power plant
Safety Enhancement
- Stress tests and accident management plans were implemented for extreme disasters to strengthen serious accident management in the aftermath of the Fukushima nuclear reactor accident in 2011.
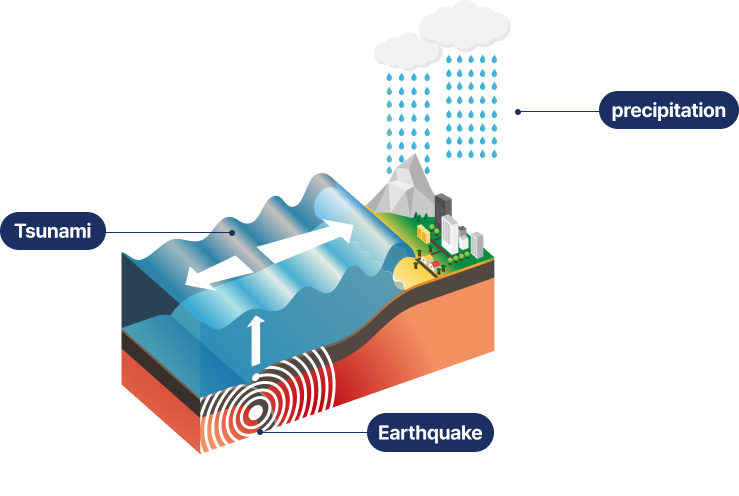
- MACST (multi-barrier accident-coping strategies) equipment is applied to prevent and mitigate multiple and severe accidents that exceed design standards in the event of extreme disasters (natural and man-made disasters) in multiple units on the same site.
Seismic Strengthening
- For earthquakes exceeding the design basis that occurred near the nuclear units, the seismic safety evaluation of safety-related structures, systems, and components (SSCs) are performed, and design changes are made to improve seismic performance of SSCs.
- Seismic safety evaluation of safety-related structures for earthquakes exceeding the design basis;
- Design changes to improve seismic performance of safety-related components at operating nuclear power plants
Design areas
- Architectural design: Engineering work related to new construction, repair, and replacement of building materials for nuclear Power plants in operation according to regulatory requirements, owner requirements, and related technical standards;
- Civil Engineering: Engineering work of new facilities in the nuclear power plants, and design changes or technical review of safety/non-safety related structures associated with the design change of the systems or new construction of maintenance facilities;
- Electrical design: Overall electrical design and engineering service related to the improvement and replacement of electrical system equipment in nuclear reactor facilities in operation;
- Instrument and control design: Application of the latest digital technology and licensing requirements to monitoring/control facilities and main control rooms to contribute to improving the safety and operability of nuclear reactor facilities;


- Mechanical design (HVAC): The HVAC design to maintain environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, pressure, ventilation, etc.) in a state suitable for using the room or specific space;
- Firefighting design: Engineering work to improve the performance of the fire extinguishing system of nuclear reactor facilities in operation according to domestic and international licensing requirements, owner requirements, and related technical standards and to replace existing fire extinguishing systems

- (Design work to replace the conventional control room with a hybrid or high-tech main control room)

- Pipeline design: Design work related to new construction, repair, and replacement of pipeline facilities for nuclear reactor facilities in operation according to licensing requirements, owner requirements, and related technical standards;
- Fluid system: Design for improving the performance of the fluid system at the nuclear reactor facilities in operation according to the relevant technical standards, licensing requirements, and project owner’s requirements
- Radiation protection: Protection of workers at onsite nuclear facilities, general residents, and the environment from radiation through design and analysis to ensure compliance with dose limits and keeping radiation exposure as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA);
- Safety analysis: Thermal hydraulic analysis is a task that evaluates thermal-hydraulic behavior due to mass, momentum, and energy flowing in and out of a finite volume. A prime example is the analysis of containment temperature, pressure, and environmental conditions during LOCA. Hazard analyses aim to achieve and maintain a safe shutdown of the power plant, from various hypothetical onsite accidents expected at the plant/facility, and minimize radioactive material leakage.